In the fast-paced world of business, where startups strive to gain a competitive edge, the development of a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) has become a key strategy. However, determining the cost of building an MVP is a crucial consideration for entrepreneurs embarking on this journey.
The expense of creating an MVP can range widely, influenced by factors such as the complexity of the app, the development team’s expertise, and the chosen technology stack. On average, building an MVP typically falls within the $10,000 to $100,000 or higher cost bracket.
In this discussion, we delve into the various factors influencing MVP costs and offer practical tips to manage and reduce these expenses effectively.
Why Knowing MVP Costs Matters for Startups:
- Realistic Budgeting: Understanding the cost of building an MVP is essential for setting realistic budget expectations. This knowledge enables startups to focus on essential features aligned with available resources and prevents overspending on non-core functionalities.
- Financial Sustainability: A clear financial plan is crucial for startups’ success, as running out of cash is a primary reason for many failures. Knowing the cost of building an MVP helps in maintaining financial sustainability.
- Securing Funding: Investors are more likely to support startups with well-defined financial plans and a clear understanding of their MVP’s potential return on investment (ROI). Knowing the cost of development enhances a startup’s ability to attract funding.
In summary, comprehending MVP development costs facilitates informed decision-making, streamlines the development process, and increases the likelihood of a successful product launch within budget constraints.
Factors Affecting MVP Development Costs:
- Complexity Level: The complexity of features, user interface (UI/UX) design, and technology stack significantly influence MVP costs.
- UI/UX Design: Allocating budget specifically for UI/UX design ensures a user-friendly product, impacting the overall MVP cost.
- Technology Stack: The choice of technology stack can affect costs, considering factors such as licensing fees and availability of skilled developers.
- Development Team: Team size, expertise level, composition, geographical location, and the decision to go in-house or outsource impact development costs.
- Development Timeframe: Keeping the development timeframe short is essential for quickly validating the core value proposition and reducing overall costs.
Hidden Costs of MVP App Development:
- Deployment and App Store Submission: Additional expenses are incurred during the preparation and submission of the MVP to app stores.
- Quality Assurance & Accessibility Testing: Rigorous testing for user experience, including accessibility services, may involve additional costs.
- Iterations and Enhancement: Incorporating user feedback and making iterative enhancements can lead to extra expenses.
- Scalability and Performance Optimization: Handling an increasing user base may require additional infrastructure resources, incurring extra costs.
- Integration and Third-Party Services: Integration with external services, APIs, or third-party platforms may involve additional fees.
- Localization and Internationalization: Adapting the MVP for global markets incurs additional design, development, and testing costs.
- Maintenance Plan: Ongoing maintenance costs are typically around 20% of overall app development costs per year.
- Growth Marketing: Promoting the MVP requires investment in growth marketing strategies, such as social media advertising and search engine optimization.
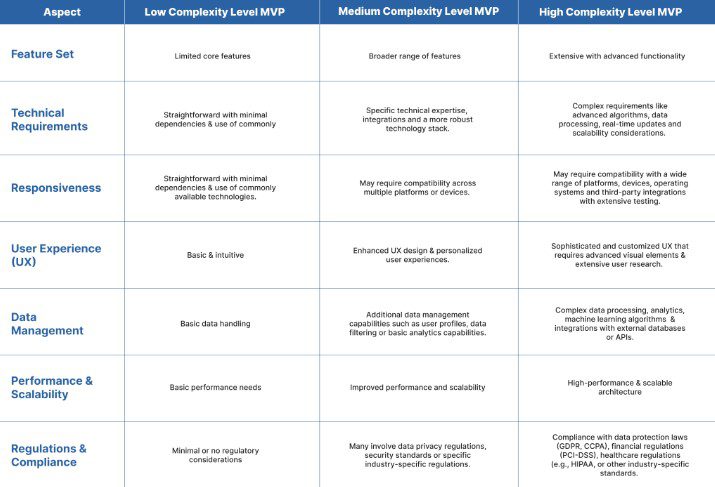
The Complexity Level of the MVP
Tips to Reduce MVP Development Costs:
Reducing Minimum Viable Product (MVP) development costs is crucial for startups and businesses aiming to launch quickly and efficiently. Here are some tips to help you cut down on costs while maintaining the essential features and quality of your MVP:
-
Focus on Core Features:
- Identify and prioritize the essential features that directly contribute to the core functionality of your product.
- Avoid unnecessary bells and whistles at this stage to keep development time and costs in check.
-
Lean Development Methodology:
- Adopt lean development principles to eliminate waste and optimize the development process.
- Emphasize rapid iterations and continuous feedback to make necessary adjustments early in the development cycle.
-
Outsource Selectively:
- Consider outsourcing certain tasks or components of your MVP to reduce labor costs. This is particularly beneficial for non-core functions.
- Ensure effective communication and collaboration with the outsourced team to maintain quality and timelines.
-
Use Open Source Tools and Frameworks:
- Leverage open-source technologies, frameworks, and libraries to save on development costs.
- This can significantly reduce the time and effort required for building common functionalities.
-
Minimum Viable Design:
- Adopt a simple and functional design for your MVP. Avoid complex and expensive design elements.
- You can enhance the design later based on user feedback and as your product gains traction.
-
Cloud Services:
- Utilize cloud services for hosting, storage, and other infrastructure needs. Cloud platforms often offer cost-effective, pay-as-you-go models.
- This eliminates the need for significant upfront hardware investments.
-
Cross-Platform Development:
- If applicable, consider cross-platform development frameworks to build your MVP for multiple platforms simultaneously. This can save development time and costs compared to native development for each platform.
-
Iterative Development:
- Start with a basic version of your MVP and gather user feedback. Use this feedback to make iterative improvements.
- This approach reduces the risk of investing heavily in features that may not resonate with your target audience.
-
Minimum Viable Team:
- Keep your development team small and focused on core competencies. A smaller team size can help control labor costs.
- Ensure that the team is skilled and experienced in the technologies required for your MVP.
-
Test Automation:
- Implement automated testing to catch bugs and issues early in the development process. This can reduce the time spent on manual testing and improve overall product quality.
-
Use MVP Development Platforms:
- Explore low-code or no-code development platforms that allow for rapid prototyping and development with minimal coding efforts.
-
Negotiate with Service Providers:
- Negotiate terms with service providers, including development tools, hosting services, and third-party integrations, to get the best possible pricing.
Remember, the goal of an MVP is to validate your business idea with minimal investment. By applying these tips, you can streamline the development process and launch your product faster and more cost-effectively.
Conclusion
Developing an MVP is a pivotal step in transforming a groundbreaking app idea into a successful product. Proper budget planning is essential, and understanding the cost of building an MVP is a key component. As multiple factors influence costs, engaging with experts is crucial for an accurate estimate. At InfoStride, we specialize in delivering high-quality and scalable MVPs, driving incremental growth for startups. Contact us to explore your MVP development journey.