Mobile app development has witnessed significant growth in recent years, and developers are constantly seeking efficient tools to create powerful applications. One such tool that has gained attention is Xamarin. In this article, we will explore the good and the bad aspects of Xamarin mobile development.
What Is Xamarin?
Xamarin is a cross-platform mobile development framework that allows developers to build applications using C# and .NET, sharing a single codebase across iOS, Android, and Windows platforms. This unique feature makes Xamarin a compelling choice for developers aiming to streamline the development process and reach a wider audience.
Pros of Using Xamarin for Development
Cross-platform Development Advantages
Xamarin allows developers to create applications that run seamlessly on multiple platforms. This eliminates the need to write separate code for iOS and Android, saving time and effort. The ability to share a significant portion of the codebase across platforms is a major advantage.
Reusability of Code
Developers appreciate Xamarin’s ability to reuse code, reducing redundancy and minimizing the chances of introducing errors. The shared codebase ensures consistency across platforms, making it easier to maintain and update applications.
Cost-effectiveness
For businesses looking to develop apps for both iOS and Android, Xamarin can be a cost-effective solution. The shared codebase means less development time, which translates to lower costs. This makes Xamarin an attractive option for startups and enterprises alike.
Xamarin Cons to Consider
Potential Performance Issues
While Xamarin offers excellent cross-platform compatibility, there can be performance considerations. Some argue that applications developed with Xamarin may not perform as well as those developed using native languages. However, advancements in Xamarin have addressed many of these concerns.
Learning Curve
Developers accustomed to other languages may face a learning curve when transitioning to C# and .NET for mobile development. While Xamarin provides a bridge for developers familiar with these technologies, there is still an initial adjustment period.
Limited Access to Some Platform-specific Features
Xamarin strives to provide a unified experience across platforms, but this can come at the cost of access to certain platform-specific features. Developers may need to find workarounds or consider alternative solutions when faced with these limitations.
Xamarin Visual Studio IDE
Certainly! Xamarin is a cross-platform mobile development framework that allows developers to create native mobile applications using C# and the .NET framework. Xamarin can be integrated with Microsoft Visual Studio, a popular integrated development environment (IDE). Here are some key points about Xamarin in Visual Studio:
- Cross-Platform Development: Xamarin enables developers to write their mobile app’s business logic in C# and share a significant portion of the codebase across multiple platforms, including iOS, Android, and Windows.
- Single Codebase: With Xamarin.Forms, developers can create a single, shared user interface (UI) for their app, which is rendered natively on each platform. This reduces the effort required to maintain separate UIs for each platform.
- Native Performance: Xamarin allows developers to achieve near-native performance since the code is compiled into native binaries for each platform. This is different from some other cross-platform frameworks that rely on web technologies.
- Visual Studio Integration: Xamarin integrates seamlessly with Microsoft Visual Studio, providing a familiar environment for developers who are already accustomed to using Visual Studio for other .NET development.
- Debugging and Profiling: Developers can use Visual Studio’s powerful debugging and profiling tools to identify and fix issues in their Xamarin apps. This includes features like step-through debugging, breakpoints, and performance profiling.
- NuGet Package Integration: Xamarin projects can leverage the extensive ecosystem of NuGet packages for adding functionality to their apps. This includes libraries for common tasks, UI controls, and other third-party components.
- Xamarin.Forms: Xamarin.Forms is a UI toolkit that allows developers to create a single, shared user interface for their app. It includes a set of common controls and layouts that map to native controls on each platform.
- Xamarin.iOS and Xamarin.Android: For more platform-specific development, developers can use Xamarin.iOS and Xamarin.Android to access native APIs and implement platform-specific features.
- Azure Integration: Xamarin apps can easily integrate with Microsoft Azure services, providing capabilities such as cloud storage, authentication, and push notifications.
- Community and Support: Xamarin has a vibrant community, and Microsoft provides extensive documentation and support for developers using Xamarin in Visual Studio.
Keep in mind that technology evolves, and there may have been updates or changes since my last training data in January 2022. Always refer to the latest documentation and release notes for the most current information.
Xamarin vs Hybrid Development vs Native iOS/Android vs Other Cross-Platform Frameworks
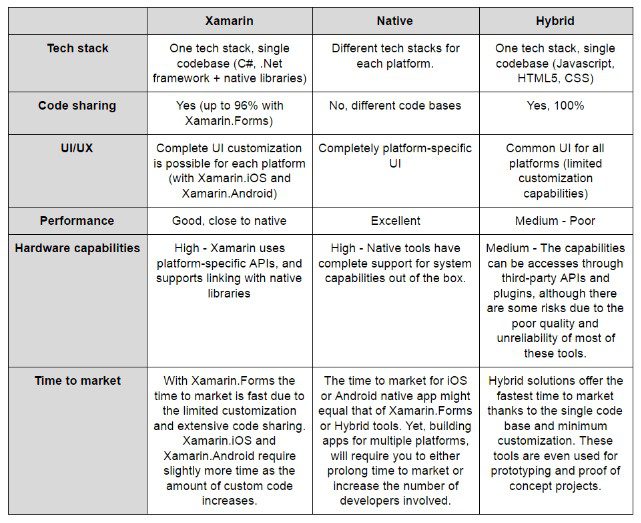
Xamarin vs Hybrid Development vs Native iOS/Android
Xamarin vs Hybrid Development
Hybrid development involves using web technologies (HTML, CSS, and JavaScript) to create mobile applications. Xamarin, on the other hand, relies on C# and .NET. The choice between Xamarin and hybrid development depends on factors such as performance requirements, development speed, and the need for native features.
Xamarin vs Native iOS/Android
Native development involves using platform-specific languages (Swift for iOS, Kotlin/Java for Android). Xamarin offers cross-platform capabilities, but native development may be preferred for applications requiring deep integration with platform-specific features.
Comparison with Other Cross-platform Frameworks
Xamarin is just one of several cross-platform frameworks available to developers. Comparisons with frameworks like Flutter, React Native, and others are essential when choosing the right tool for a specific project.
Piece of Advice
While Xamarin has its advantages, it may not be the perfect fit for every project. Consider Xamarin when:
- Cross-platform compatibility is crucial.
- Code reusability is a priority.
- Development time and cost need to be minimized.
However, for projects with a strong focus on platform-specific features or those requiring peak performance, native development might be a more suitable choice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Xamarin is a powerful tool for cross-platform mobile development, offering numerous advantages such as code reusability and cost-effectiveness. However, developers must weigh these benefits against potential drawbacks like a learning curve and limited access to platform-specific features. Choosing Xamarin should align with the project’s specific needs and goals.