- Home
- App Development Services
- What is XR & what is...
The landscape of the mobile app market is undergoing a transformative shift with the emergence of Extended Reality (XR). XR holds the promise of revolutionizing the way users interact with digital content on their mobile devices, presenting novel and engaging possibilities.
In the context of Extended Reality (XR), “Virtuality” refers to the degree of immersion or realism experienced by users in a digital environment. It is often used to describe a spectrum of experiences ranging from the completely virtual to the entirely real. The concept is commonly divided into three main categories:
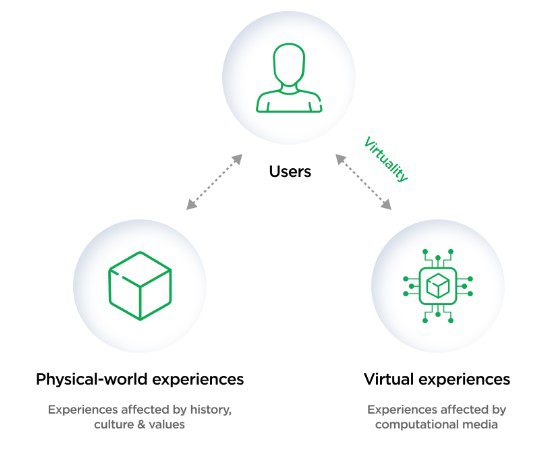
Virtuality: Is the state of being brought about by being simulated using a computer
The emergence of these virtuality concepts, especially in the form of XR, is shaping the landscape of the mobile app market by introducing new and innovative ways for users to engage with digital content. Whether through immersive VR experiences, context-aware AR applications, or the integration of virtual elements into the real world via MR, virtuality is expanding the possibilities for mobile app developers and creating exciting opportunities for users to interact with digital content in more immersive and meaningful ways.
Delving into the umbrella term “XR,” which encompasses Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR), this section dissects the distinctive features and characteristics of these technologies.
Understanding XR as a medium of communication, we examine the four key characteristics outlined by J. H. Murray. These characteristics, namely procedural affordances, participatory affordances, encyclopedic affordances, and spatial affordances, lay the foundation for designing immersive and interactive XR experiences.
Highlighting the fundamental elements of XR technology, this section elucidates how 3D models and computer-generated imagery (CGI) form the backbone of all virtual experiences. The focus is on VR, AR, and MR, each with its unique application and device requirements.
Illustrating the practical application of XR, particularly in AR experiences, this section showcases examples of AR designs for social events, offering insights into the versatility and creative potential of XR technology.
Expanding on the diverse applications of XR, this section explores examples across various industries, from gaming with Pokemon Go to utilitarian solutions like IKEA Place and educational platforms like Complete Anatomy.
Concluding the exploration of XR technologies, the article underscores the transformative potential of XR in reshaping the mobile app market. By providing immersive and interactive experiences, XR stands poised to revolutionize user engagement with digital content on mobile devices, opening up new dimensions in virtual shopping, gaming, and education. As technologies advance and accessibility increases, a surge of innovative powered mobile apps is anticipated, transforming the way users interact with their devices and the digital world.
© 2013 - 2025 Foreignerds. All Rights Reserved